Ear candling has gained popularity as a natural remedy, often touted for removing earwax, alleviating pressure, and even improving hearing.
Its appeal comes from being marketed as a gentle, spa-like treatment with a detoxifying effect. Supporters believe the hollow candle creates suction to pull out impurities, offering relaxation and relief.
But does it actually deliver on those claims? Scientific research shows mixed results, and medical experts raise serious concerns about safety.
From burns and blockages to hearing damage, the risks can outweigh the promised benefits. Understanding what’s real and what’s myth is key before considering this practice.
What Is Ear Candling?
Ear candling, also known as ear coning or Hopi ear candling, is an alternative therapy where a hollow, cone-shaped candle made of cotton or muslin, coated in wax (typically beeswax, paraffin, or soy), is inserted into the ear canal.
The wide end is lit while the narrow end rests in the ear, with the user lying on their side.
Each candle is approximately 10 inches long and may contain herbs or essential oils, such as chamomile or rosemary. To prevent burns, a foil guard or a paper plate is often used.
Supporters who wonder, Do ear candles work?
believe the heat creates suction that removes wax, relieves sinus pressure, eases tinnitus, and even detoxifies the body.
How Do Ear Candles Work?

Advocates often ask, How do ear candles work? and describe the process as creating a vacuum effect inside the hollow candle.
They claim that the flame generates heat, which pulls earwax, debris, and moisture out of the ear canal, thereby loosening blockages.
Some also believe ear candling improves circulation, reduces ear and sinus discomfort, and promotes overall relaxation.
After a session, practitioners frequently cut open the candle stub, pointing to dark residue inside as proof of wax removal.
However, scientific testing suggests this residue comes from the candle itself rather than earwax, raising doubts about whether the method works as claimed.
What Does Scientific Evidence Say?
Numerous scientific studies and expert reviews have thoroughly investigated ear candling, consistently finding it ineffective and potentially dangerous.
- Research shows that no vacuum or suction effect is created during the process. Instead, the residue often found inside a used candle is mostly burnt wax and fabric, not earwax from the ear canal.
- A well-known 1996 study published in The Laryngoscope demonstrated that ear candling did not remove earwax but instead deposited candle wax into the ear canal, potentially worsening blockages.
- Additional case reports, such as one in the Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, describe patients suffering burns, wax occlusion, and even hearing loss after the procedure.
- Clinical experts emphasize that ear candling does not improve hearing, cure infections, or remove toxins. Trusted sources, such as Healthline, WebMD, and Verywell Health, provide detailed overviews that confirm these findings.
In short, ear candling is unsafe, ineffective, and not recommended; safer, medically proven methods exist for maintaining ear health and removing earwax.
Are Ear Candles Safe?
The FDA and numerous health organizations warn against ear candling because it carries significant risks:
- Burn injuries to the face, external ear, ear canal, or even the eardrum, caused by hot candle wax or flames.
- Punctured eardrums from candle insertion or wax pushing deeper.
- Ear blockages or infections caused by dripping candle wax lodging in the ear canal.
- Risk of accidental fires and burns to hair, face, or surrounding areas due to open flames near the head.
- Delayed medical care for true infections or hearing loss symptoms, as users may rely on this ineffective treatment.
Multiple anecdotal injury reports and case studies document burns, eardrum perforations, and worsening earwax blockages following ear candle use.
These dangers occur even when users follow instructions carefully.
Myths vs. Reality of Ear Candling
Many claims have been made about ear candling, but most don’t hold up when tested against science and medical evidence.
Below is a clear comparison of common myths versus the actual reality.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Ear candling pulls out earwax and toxins | No suction is created; residue is simply burnt candle wax |
| Ear candles improve hearing and sinus issues | Not supported by scientific evidence or clinical trials |
| Ear candling is safe because it’s a natural remedy | Natural products can still cause burns, injuries, or blockages |
In reality, ear candling offers no proven benefits and carries avoidable risks, making professional care the only safe choice.
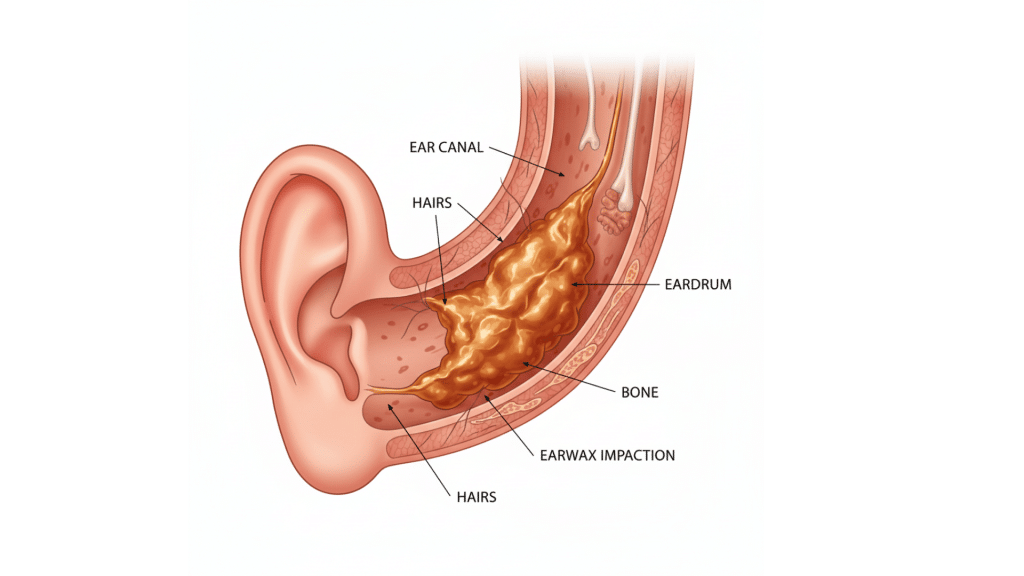
When Might Earwax Become a Problem?
Earwax (cerumen) is a natural secretion that protects, cleans, and lubricates the ear canal. Most people do not require routine removal, as the ear self-cleans by naturally shedding wax outward.
However, issues such as impaction, when wax is hardened and blocks the ear canal, may cause:
- Hearing loss or muffled sounds
- Earache or a feeling of fullness
- Itching or odor
- Dizziness or tinnitus
Signs that professional care is needed include persistent discomfort, pain, discharge, or sudden changes in hearing.
Safer and Evidence-Based Alternatives for Earwax Removal

If you’re considering options beyond ear candling, there are several safe, medically approved methods to manage earwax.
These approaches are backed by research, widely recommended by health professionals, and much safer than burning candles near your ear.
1. Ear Drops or Wax-Softening Solutions
Over-the-counter drops containing mineral oil, olive oil, hydrogen peroxide, saline, or glycerin can gradually soften hardened earwax.
This makes natural expulsion easier and reduces the need for more invasive procedures, offering a gentle, at-home option for mild buildup.
2. Ear Irrigation
Using a rubber bulb syringe filled with warm water, ear irrigation gently flushes softened wax out of the canal.
While effective, it must be avoided in cases of ear injury, perforated eardrum, or chronic ear infections to prevent complications.
3. Professional Ear Cleaning
An ENT specialist or audiologist can remove stubborn or impacted wax using specialized tools such as suction devices, curettes, or irrigation systems.
This method is considered the safest and most effective, particularly when home remedies are not successful.
4. Avoid Cotton Swabs or Sharp Objects
Inserting cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other sharp objects into the ear canal usually pushes wax deeper.
This increases the risk of impaction, infection, and even eardrum damage, making it one of the most harmful habits to avoid.
Regulatory and Medical Recommendations
Global health authorities strongly discourage the use of ear candles due to safety concerns and lack of proven benefits.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has repeatedly warned that ear candling is ineffective and poses risks, including burns, damage to the ear canal, and hearing loss.
Similarly, the American Academy of Otolaryngology and other hearing health organizations do not recommend this practice, emphasizing that it offers no therapeutic value.
In countries such as Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has also flagged safety issues.
Although ear candles may remain available for purchase in some regions, medical professionals and regulatory agencies consistently advise against their use.
Final Thoughts
Ear candling may appear harmless or even relaxing, but the reality is that it introduces unnecessary risks without delivering meaningful results.
Your ear health deserves safe, effective care, not methods that can leave you worse off than before.
If you’re experiencing earwax buildup, discomfort, or hearing changes, consult a qualified healthcare professional who can provide safe and tailored solutions to address your specific needs.
Options like ear drops, irrigation, or expert removal are proven and reliable. Protecting your hearing means choosing science-backed care.
Skip the candles, trust your ears to real medicine, and prioritize your long-term hearing health starting today.