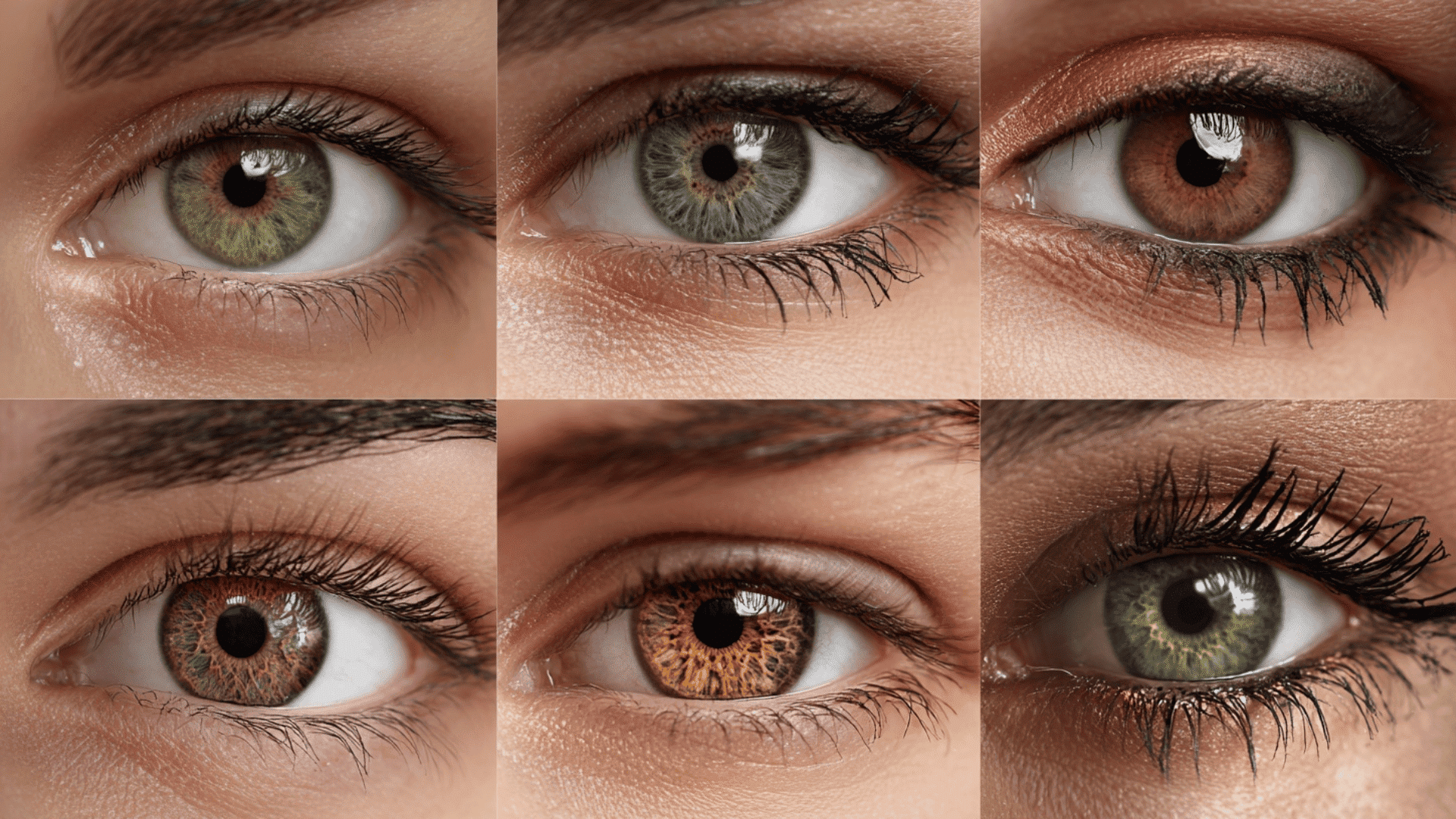
Hazel eyes are among the most beautiful and mysterious eye colors in the world.
Unlike solid shades of blue, brown, or green, hazel eyes display a dynamic blend of tones that shift in response to lighting and pupil dilation.
Many people are amazed by the science behind hazel eyes, often wondering what makes them so distinctive.
From warm, golden browns to rare, green hazel eyes, each variation tells a story rooted in genetics and pigmentation.
You’ll learn about the different types of hazel eyes, the genetic factors behind their diversity, and their cultural rarity and beauty by the end of this.
What Makes Hazel Eyes Unique?
Hazel eyes stand out because they are not a single color. Instead, they showcase a beautiful blend of brown, green, and amber tones that harmoniously combine in the iris.
This creates a multicolored appearance that sets them apart from eyes that are pure brown, green, or amber. The unique look of hazel eyes is attributed to how light interacts with the iris.
The iris contains different amounts of a pigment called melanin. In hazel eyes, melanin is distributed unevenly throughout the iris layers. This uneven distribution creates the mixed colors we see.
Hazel eyes have a moderate, uneven melanin distribution that creates a layered appearance, causing their color to shift with changes in light.
How Do Hazel Eyes Get Their Color?
Hazel eyes derive their unique color from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Their appearance shifts based on factors beyond DNA alone.
This is why hazel eyes often seem to change shades in different situations, adding to their intrigue.
Non-Genetic Factors of Hazel Eyes
While genetics provides the base, non-genetic influences also shape their look:
-
Lighting & Surroundings: Sunlight, indoor light, clothing, and makeup can highlight green, gold, or brown tones differently.
-
Pupil Size & Age: Dilated pupils reveal more blended colors, while aging or health changes may subtly shift pigmentation.
The Genetics Behind Hazel Eyes
Hazel eyes are a polygenic trait, meaning multiple genes work together to produce their unique blend of colors.
Unlike brown, blue, or green eyes, which are influenced more directly by specific melanin levels, hazel eyes result from a complex interaction of several genes.
1. OCA2: The Brown Eye Gene
- Controls melanin production in the iris, with higher levels resulting in brown eyes and lower levels allowing for lighter shades.
- Variations in melanin cause uneven distribution, producing a mix of brown, green, and golden tones typical of hazel eyes.
2. HERC2: The Switch Gene
- Regulates OCA2, controlling melanin production in various iris areas.
- Creates patchy melanin distribution, where brown, green, or gold tones appear depending on light scattering.
3. Other Genes Influencing Hazel Eyes
- Genes such as TYR, TYRP1, and IRF4 influence the production and processing of melanin.
- Their variations explain why hazel eyes can lean brown, green, or gold, even within the same family.
This genetic complexity is what makes hazel eyes so diverse. The way multiple genes interact not only explains their shifting shades of green, gold, and brown but also why no two hazel eyes ever look exactly alike.
Different Types of Hazel Eyes
Hazel eyes come in several distinct variations, each with its own unique characteristics and beauty. Understanding these different types helps explain the wide range of appearances within the hazel eye category.
1. Brown-Dominant Hazel
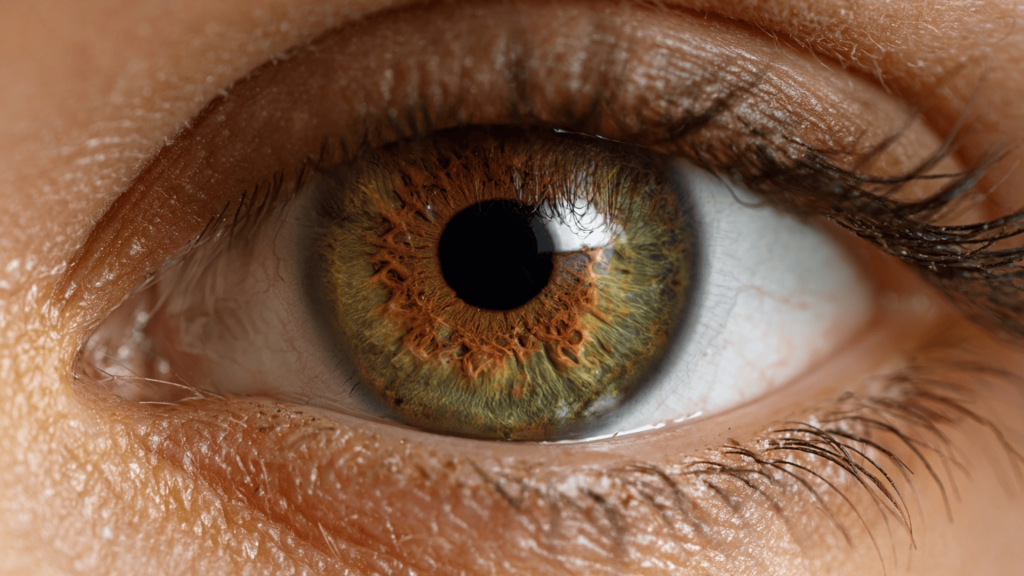

Brown-dominant hazel eyes are the most common type of hazel eyes. These eyes appear mostly brown but contain noticeable flecks of green or gold scattered throughout the iris.
The brown color usually forms a ring around the pupil, with lighter green or golden tones appearing toward the outer edge of the iris.
This type often looks warm and earthy, with the brown providing a rich base for the other colors to shine through.
2. Green-Dominant Hazel
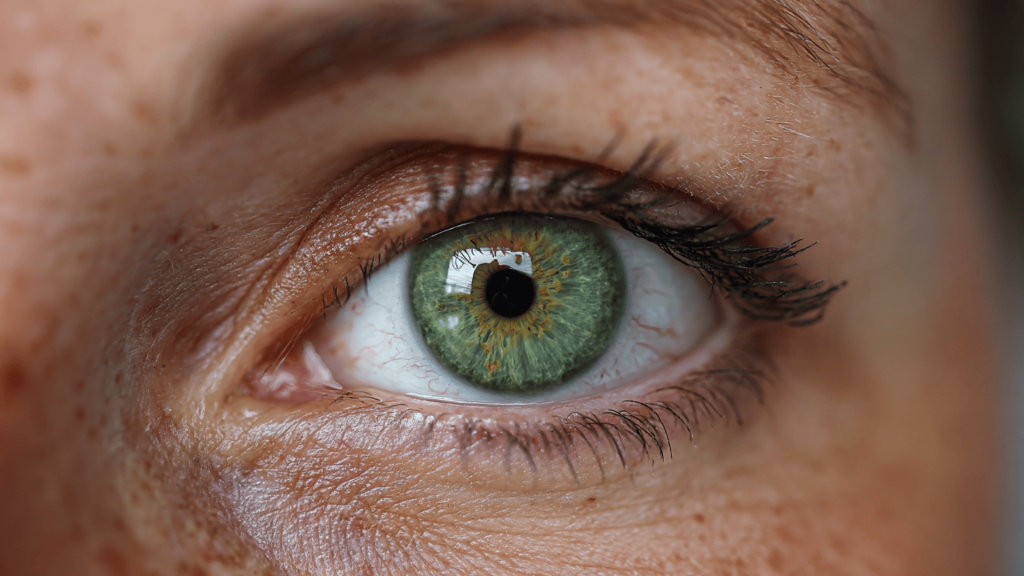

Green-Dominant Hazel is less common and features green as the primary color with touches of brown or amber mixed in. These eyes often have a ring of brown around the pupil that blends into green toward the outer iris.
Sometimes, golden or amber flecks appear throughout the green areas, creating a forest-like appearance. This type is particularly striking because the green color is more prominent than in other hazel variations.
3. Golden/Amber Hazel
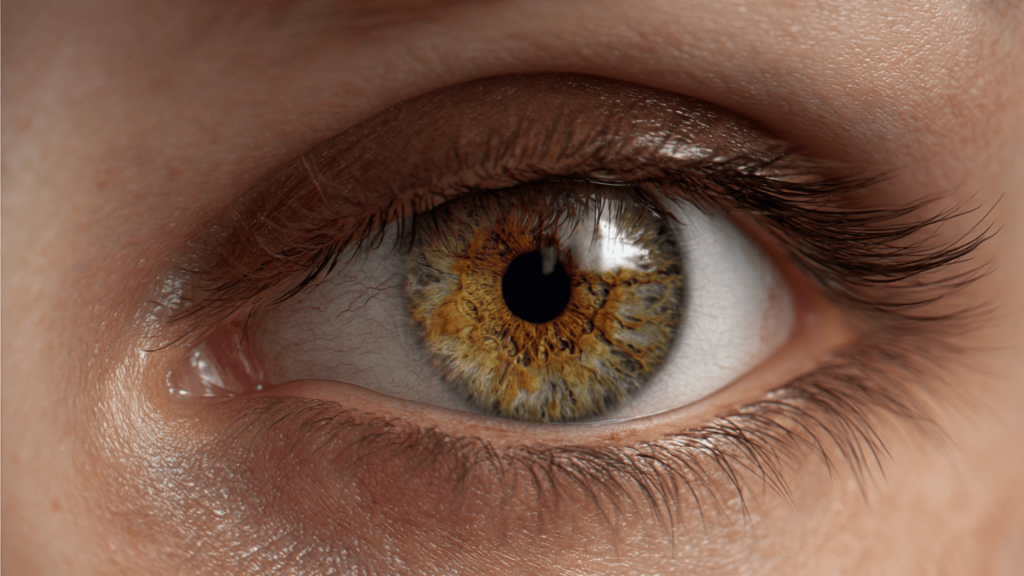
Golden/Amber Hazel eyes showcase rich golden and amber tones as their main colors. These eyes often have a warm, honey-like appearance with subtle hints of green or light brown.
The golden color can be very vibrant, especially in bright light, making these eyes appear almost to glow. This type is often associated with warmth and brightness.
4. Mixed Hazel
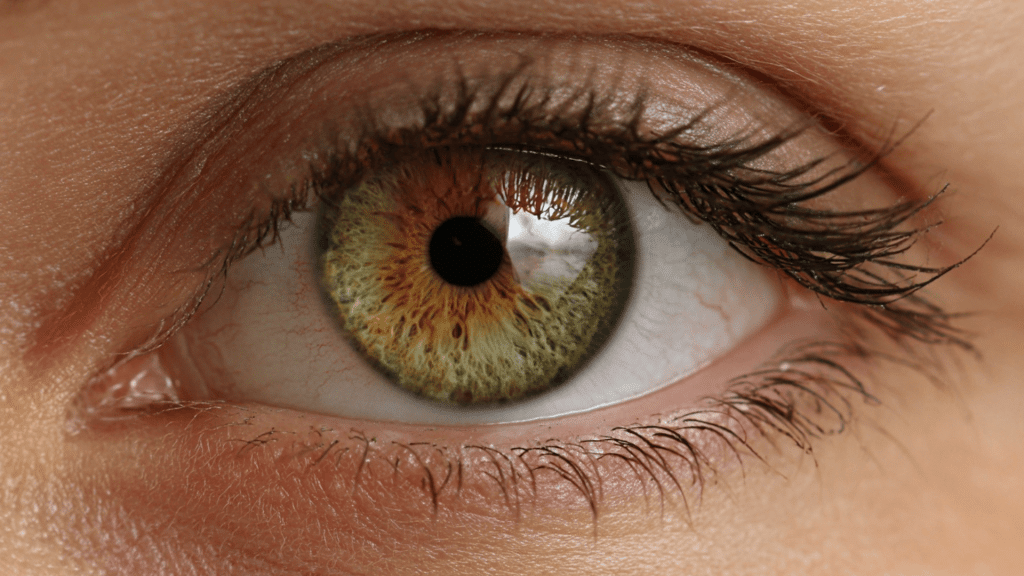
Mixed Hazel represents the most balanced type of hazel eyes, where green, gold, and brown appear in roughly equal amounts throughout the iris.
These eyes truly demonstrate the changing nature of hazel eyes, as they can appear more green in some lighting, more brown in others, and golden in bright sunlight.
The colors often swirl together in complex patterns, making each eye unique.
5. Rare Green Hazel Eyes
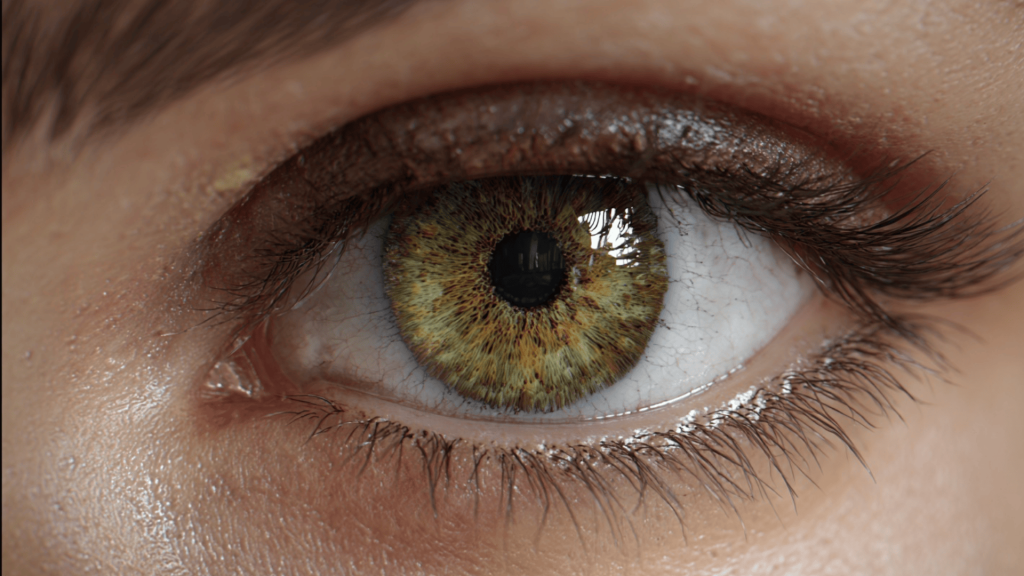

Green hazel eyes are the rarest variation of hazel, blending dominant green with subtle flecks of brown or amber. This striking appearance results from low melanin, allowing green tones to emerge, while scattered melanin creates golden accents.
Light scattering improves the effect. Found in less than 10% of the global population, they’ve long symbolized mystery and allure in culture.
Cultural Perceptions of Hazel Eyes
- Ancient Admiration: Hazel eyes have long intrigued artists, writers, and cultures, symbolizing mystery and beauty.
- Literary portrayals: Characters with hazel eyes are often shown as complex, independent, or mysterious, representing depth and hidden qualities.
- Cultural symbolism: In some cultures, hazel eyes are associated with wisdom and intelligence, while others link them to creativity and artistic ability.
- Symbol of adaptability: The shifting colors of hazel eyes are often viewed as signs of adaptability and strength.
- Regional perceptions: In brown-eye-dominant regions, hazel eyes are seen as exotic and attractive, while in lighter-eye regions, they’re admired for uniqueness and depth.
- Modern beauty standards: Hazel eyes are celebrated for their versatility, as they easily complement a wide range of makeup looks and clothing styles.
Hazel Eyes and Light Interaction
Hazel eyes often shift between green, gold, and brown depending on the light and surroundings. This chameleon-like quality is one of the reasons they’re considered so unique and mysterious.
The effect is created by light reflecting off different layers of the iris, each with varying melanin levels, resulting in a dynamic play of colors. Here are the key factors that influence their look:
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Bright Sunlight | Show golden and amber tones |
| Fluorescent Light | Brings out green or brown shades |
| Warm Lighting | Highlights brown and golden hues |
| Outdoor Light | Often emphasizes green tones |
| Clothing Colors | Green makes green pop; gold/brown deepen tones |
| Pupil Size | Dilated shows more blend; constricted sharpens colors |
This shifting effect makes hazel eyes unique, giving them a mysterious, ever-changing beauty that adapts to light and surroundings.
Final Thoughts
Hazel eyes remain one of nature’s most beautiful genetic outcomes, blending colors in a way that no two sets of eyes look exactly alike.
From brown-dominant shades to rare green hazel eyes, the diversity within hazel eye types reflects the complex science of genetics and pigmentation.
Their rarity and ability to shift colors under different conditions make them truly charming. What should you remember about hazel eyes?
They represent a perfect example of how genetics and light work together to create natural beauty.
Understanding their science deepens our appreciation for these mesmerizing windows to the soul, reminding us that some of nature’s most beautiful creations come from the most complex processes.






